Credit Card ISO Adoption
Introduction:
The Credit Card Industry has been vital to modern-day commerce, facilitating seamless transactions and driving economic growth. With the emergence of the ISO 20022 messaging standard, the landscape of credit card business operations is poised for significant transformation. This article explores the potential impact of ISO 20022 adoption on the credit card business, highlighting the key advantages, challenges, and implications for stakeholders. ISO 8583 allowed for greater interoperability across payment networks (it remains the primary standard for retail card transactions internationally), and the flexible data format easily accommodated new products and services, such as debit and enhanced security and authorization (Stearns, 2013). Similarly, new messaging standards were being developed in the securities and high-value transaction space, such as ISO 15022 (Securities — Scheme for Messages) and its predecessor ISO 7775. While these messaging standards have enabled payment infrastructure connections around the world, some friction remains, notably around cross-border payments (particularly large-value and remittance payments) (Financial Stability Board, 2020). In particular, domestic standards — as opposed to internationally accepted standards — for payments continue to be a significant impediment to cross-border interoperability (Gallaher, Cory, and Ahmed, 2020). Other governance-related challenges (eg transparency issues, conflicting standards for combating money laundering and financing terrorism, etc) also create friction, as do certain technical challenges related to limited clearing hours (Financial Stability Board, 2020). Additionally, with the expansion of new payment products and technologies, a more flexible and expandable messaging standard is needed to handle richer data. While current messaging standards allow for some flexibility, they are not always able to pass along enough information to ensure straight-through processing without manual intervention. As governments and the financial sector work to modernize payment systems, many are looking to address some of these issues with a new standard: ISO 20022. In what follows, this article explores why this standard is being adopted, how it is being implemented, and its perceived benefits and limitations.
The differences between ISO 8583 and ISO 20022
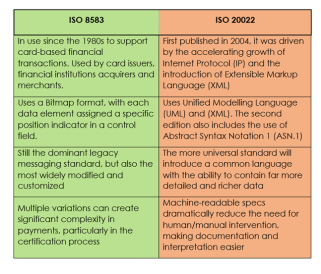
We will discuss the key differences between ISO 8583 and ISO 20022, focusing on how ISO 20022 covers all transactions, while ISO 8583 is specific to card-based financial transactions. Although ISO 8583 remains the messaging standard for card-based payments, the retail payment industry and the financial industry are undergoing a digital transformation, emphasizing the need for a global standard. In this article, we will discuss the key differences between ISO 8583 and ISO 20022, focusing on how ISO 20022 covers all transactions, while ISO 8583 is specific to card-based financial transactions. Although ISO 8583 remains the messaging standard for card-based payments, the retail payment industry and the financial industry as a whole are undergoing a digital transformation, emphasizing the need for a global standard.
What is ISO 8583?
As briefly covered earlier in this article, the ISO 8583 messaging protocol is used for retail payment systems that process credit and debit card transactions initiated by cardholders using payment cards such as Visa and Mastercard. Basically, when a cardholder uses a payment card, the electronic transaction data is exchanged throughout the network using ISO 8583 data elements, messages, and code values. The ISO 8583 standard is officially titled “Financial Transaction Card-Originated Messages — Interchange Message Specifications”.
How does ISO 8583 work?
The ISO 8583 standard is typically used by POS devices and ATMs. The messages themselves commonly contain data including, where it originated, card account number, and bank sort code. Some of the applications that use the data transmitted by ISO 8583 include:
- Purchases
- Withdrawals
- Deposits
- Reversals
- Refunds
- Balance inquiry
- Payments
- Inter-account transfers
ISO 8583 uses a bitmap format, assigning each data element a definite position indicator in a control field.
ISO 8583 also defines point-to-point messages for totals reconciliation, network sign-on and sign-off as well as other administrative messages.
Prior to ISO 20022, corporate payments (which used SWIFT messaging) and retail payments (which used ISO 8583) had no commonality. The introduction of ISO 20022 is an attempt to bring a number of legacy message formats into a common structure.
The world relies on data
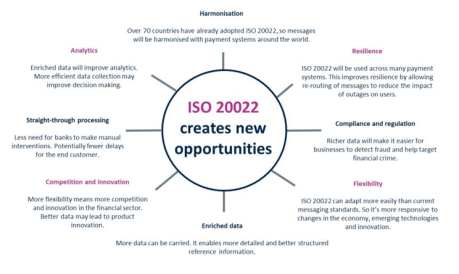
More than ever, payment networks rely heavily on data to process payments, therefore the universal adoption of the ISO 20022 messaging standard is aimed at simplifying that data while bringing a number of legacy message formats into a common, easy-to-understand structure. ISO 20022 allows for the transmission of richer, more detailed data, enabling targeted analytics, which equates to gold in the finance and payment world.
Why is ISO 20022 adoption important?
The adoption of ISO 20022 brings significant improvements to payment processing capabilities including faster and more accurate processing and enhanced reconciliation processes due to increased data richness and improved analytics.
A summary of the key benefits of ISO 20022
- ISO 20022 provides a common structure and language for financial business process communications.
- Enables superior interoperability with other protocols.
- Generates a financial message standard that encompasses complete transaction sequences.
- Includes a complete selection of data elements, institution identification codes and messages for investment funds.
- The ISO 20022 standard will provide longer references for non-Latin alphabets, with a character set ten times larger than SWIFT MT messages and carrying a great deal more information.
- Offers financial institutions improved remittance and permitting for extensions.
- It can effectively manage formats not previously allowed for cross-operation, creating better interoperability.
Prior to ISO 20022, corporate payments (which used SWIFT messaging) and retail payments (which used ISO 8583) had no commonality. The introduction of ISO 20022 is an attempt to bring a number of legacy message formats into a common structure.
Benefits of a common, integrated messaging structure
The transition to ISO 20022 signals that it’s time for the retail payments industry to embrace the benefits of adopting a single common messaging structure. Due to multiple variations of the ISO 8583 standard, it can cause a great deal of complexity, particularly with the certification process, which often requires the need for human intervention, documentation, and interpretation of the standard. With ISO 20022, transaction information is machine-readable and will significantly streamline the payments messaging process.
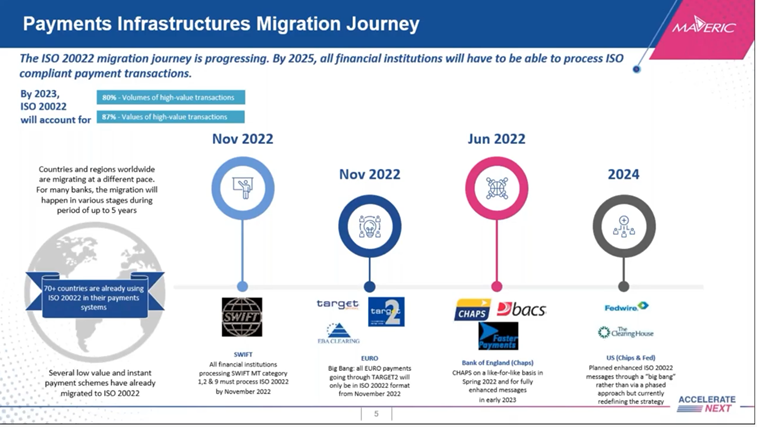
Image source: Temenos payments hub (webinar)
Conclusion:
The adoption of ISO 20022 in the credit card business holds immense potential for transformative change. The standard’s enhanced payment processing capabilities, increased data richness, improved security, and streamlined reconciliation processes offer significant benefits to stakeholders. While challenges exist, proactive planning, collaboration, and investment in technological infrastructure can help organizations harness the full potential of ISO 20022 and unlock new opportunities in the dynamic credit card industry.

